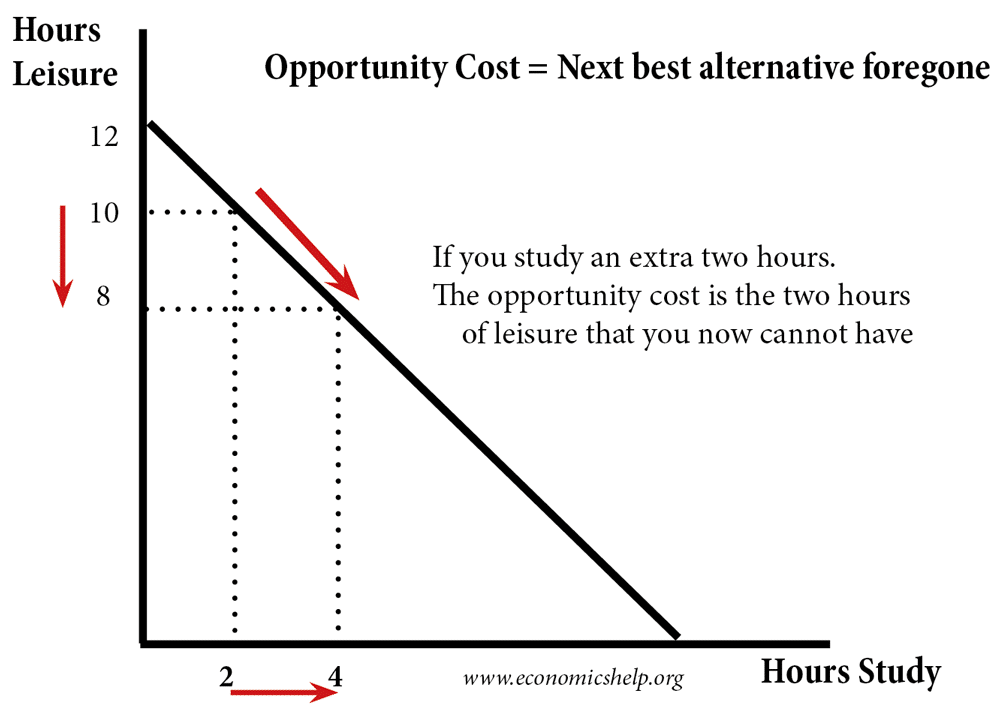
The last step of developing a master budget uses the components you have compiled to create a budgeted balance sheet. The budgeted balance sheet predicts the final effect of costs and sales on the company’s balance sheet. A master budget includes all of the lower-level budgets within an organization. It gives a firm a broad overview of its finances and is often used as a central planning tool.
They can take necessary steps to manage their cash flow, such as delaying payments or arranging short-term financing. Depreciation is deducted at the bottom of the manufacturing overhead budget to determine cash payments for overhead because depreciation is not a cash transaction. Budgeting is an essential function of any business, necessary for both financial planning and growth. A master budget gathers a company’s lower-level budgets and incorporates them into one central document for ease of reference. Keep reading for a closer look at what’s included in a master budget, as well as how to use it.
Master Budget Explained: Component, Examples, and How to Prepare – Recommended Reading
This blog post will delve into what a master budget is, its importance for businesses, who is responsible for creating it, and what skills they need. We will also discuss the key components of a master budget, provide an example, and look at some of the common challenges businesses face when preparing a master budget. Spreadsheet programs are not the only way managers use technology to facilitate the budgeting process.
- Likewise, it is used in estimating the overall profitability as well as asset and liability position.
- Some of these do not directly derive from the sales that the firm will have because they are mostly fixed in nature.
- Cloud-based software can be accessed via the Internet, making it easier for businesses to collaborate and share financial data.
- The last part of the Annual Business Plan is the Investment or Capital Budget.
- The production side submits their budget as well for the cost of manufacturing the tools to be sold.
Any item that is not in cash, such as depreciation, is ignored by the cash budget. A business might also want to keep a minimum level of cash in case of emergencies. These assumptions facilitate the planning process by removing many of the economic complexities. It’s great to be optimistic about your business, but an overly optimistic budget does no one any favors. Once you have sales projections down, many of the other budgets fall into place. The Cash Budget is an important piece of the Master Budget, as it illustrates the company’s expected liquidity indicators.
The role of the master budget
We begin the budget process by discussing the planned operating budget or projected income statement. Lord’s firm helps venture-backed startups create financial plans and master budgets. Master budgets are important because they serve as a planning tool to guide the company’s actions in the upcoming time period.
A master budget will show all the details of the company’s income-generating actions via the operating budget, with an overview of revenue and expenses. It will also show cash inflows and outflows from the cash flow statement, and estimations of what will appear on the balance sheet at the end of the accounting period. The master budget allows company directors to forecast the actions they will need to take in the upcoming quarter or year to meet their goals. A financial budget consists of the cash budget, the budgeted balance sheet, and the budget for capital expenses. Similar to the individual budgets that make up the operating budgets, the financial budgets serve to assist with planning and monitoring the financing / cash requirements of the business.
Cash Payments for Purchases of Materials
If you’re not manufacturing items, you can skip the production budget and focus on the materials budget instead. A master budget is a comprehensive budget created from a series of smaller, specialized business budgets. The master budget process has two parts — an operating budget and a financial budget — that are themselves made up of a series of smaller budgets. Any company that wants to run effectively and efficiently prepares budgets for the fiscal year. This allows for an overarching view of how the finances will look for that period of time. When companies have several departments, the need for a master budget arises.
This can occur when businesses base their revenue projections on unrealistic assumptions, such as assuming that sales will grow exponentially without considering market conditions or competitors. To avoid this mistake, businesses should base their revenue projections on historical data, market research, and other relevant factors. A master budget provides a clear picture of the company’s current and projected financial situation. This helps businesses identify potential risks and areas where they can cut costs, allowing them to better understand their financial standing in times of crisis. However, many businesses do not have dedicated financial staff or may not have the experience necessary to create an adequate budget.
The drawback is that managers may not fully understand or may misunderstand the strategic plan. The desired ending inventory is usually based on the next period’s sales budget. Considerations involve the time required to produce the product, (i.e., cycle time or lead time) as well as setup costs and carrying costs. In a just-in-time environment the desired Master budget ending inventory is relatively small, or theoretically zero in a perfect situation. In the examples and problems in this chapter, the ending finished goods inventory is stated as a percentage of the next period’s (month’s) unit sales. Thus, it is used to integrate and coordinate the activities of the various functional areas within the organization.
Step 2: Create a production budget
Once again, depreciation is deducted at the bottom of this budget to determine cash payments for selling and administrative costs, which we use later in the chapter for the cash budget. The company must determine the number of sales the company expects to make in the next year. Then, it must budget how many sales in units it needs to make to meet the sales budget and meet-ending inventory requirements. Most companies have an ending inventory they want to meet every month or quarter so that they don’t stock out. Accountants and financial managers are concerned daily about the cost implications of decisions and activities, but many other managers are not.
This allows businesses to make informed strategic decisions about their operations, such as investing in new products or expanding into new markets. With a long-term view, businesses can better assess these decisions’ potential risks and rewards. By regularly reviewing and updating the master budget, businesses can make informed decisions about their operations. They can change their spending and investment plans to remain financially stable, allowing them to react quickly to unforeseen events. By regularly reviewing the master budget, businesses can gather data and insights that can be used to improve forecasting accuracy.
More specifically, it compiles the business units’, departments’, and cost centers’ expectations and consolidates them in Budgeted financial statements. To a certain extent, The Master Budget resembles the Annual Report of a company. However, while any Annual Report looks into the past and depicts the firm’s historical performance, the Master Budget is all about the future of an organization.
Cloud-based software can be accessed via the Internet, making it easier for businesses to collaborate and share financial data. These tools also provide real-time updates, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring accuracy. The first step in aligning the master budget with strategic goals is to set clear, measurable objectives. These objectives should be specific, achievable, and aligned with the company’s vision and mission. Once the goals are established, the master budget can be developed to support them. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the master budget can help businesses optimize resource allocation.
With the right skills, knowledge, and tools, businesses can create a master budget that helps them achieve long-term financial success and sustainably contribute to society. However, creating a master budget can be challenging, and businesses must consider ethical considerations, engage stakeholders, and leverage technology to streamline and automate the process. By doing so, businesses can create a master budget that benefits all stakeholders and contributes to the common good.
To avoid this mistake, businesses should carefully consider their cash flow projections and ensure they have enough cash to cover their expenses. To ensure that the master budget aligns with strategic goals, it is essential to involve key stakeholders in the budgeting process. Their input can provide valuable insights into the resources needed to achieve the strategic goals. For example, adjusting the sales budget and related budgets such as production, labor, and overhead may be necessary if sales are lower than expected.
A capital expenditure budget will have information regarding the purchase or sale of any large assets. Companies plan their capital expenditures out well in advance due to the sheer amount of money and or time that projects in this category tend to involve. At its most fundamental level, financial planning as a whole begins with selecting a budgeting method. By now, you should know that we could either use the bottom-up or the top-down approach. Once you have that out of the way, you are ready to calculate projected sales.
Your Guide To Earning A Master’s Degree In Economics – Forbes … – Forbes
Your Guide To Earning A Master’s Degree In Economics – Forbes ….
Posted: Wed, 16 Aug 2023 14:35:38 GMT [source]
Similarly, if costs are higher than expected, it may be necessary to revise the operating and overhead budgets to reflect the increased expenses. Monthly updates suit businesses with a complex financial planning cycle, such as those with multiple products, services, or revenue streams. Monthly updates allow businesses to track their financial performance in real-time and make informed decisions based on the available data.



